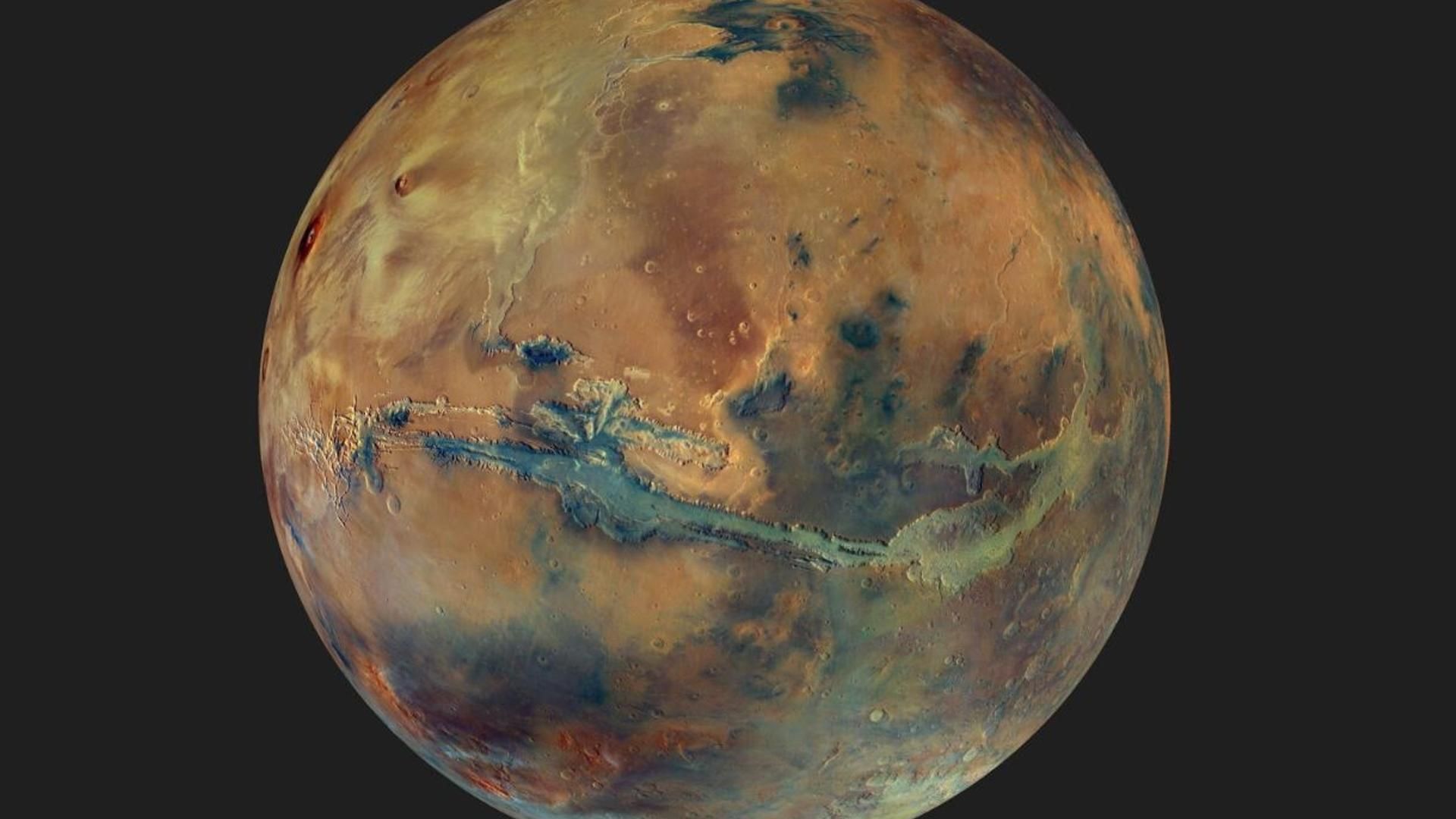
To see the planet extra broadly, HRSC assembled 90 photographs at increased altitudes (4,000 to 10,000 km). These large-scale photographs are usually obtained to watch climate patterns on Mars. So far, suppression of this impact throughout picture processing has lowered colour variations between totally different components of Mars
A brand new mosaic of Mars from the HRSC digital camera marks 20 years because the launch of ESA’s Mars Express orbiter, revealing the planet’s colour and composition in spectacular element.
HRSC (High Resolution Stereo Camera) usually pictures the floor of Mars from an altitude of about 300 km, the closest the spacecraft will get to Mars in its elliptical orbit, and the ensuing photographs cowl areas about 50 km huge.
However, the mosaic introduced right here makes use of a barely totally different strategy. To see the planet extra broadly, HRSC assembled 90 photographs at increased altitudes (4,000 to 10,000 km), thus capturing areas round 2,500 km huge. These photographs had been then put collectively to type an entire world view.
These large-scale photographs are usually obtained to watch climate patterns on Mars. The new view highlights variation on the floor of Mars by enhancing native colour and distinction.
Thanks to its 9 picture channels, HRSC can visualize Mars not solely in three dimensions but additionally in colour. However, the ever-changing opacity of the Martian ambiance makes it troublesome to precisely decide floor colours from orbit. Dust scatters and displays gentle, inflicting colours to alter from picture to picture and making a mosaic impact when mosaicking collectively.
So far, suppressing this impact throughout picture processing has lowered colour variations between totally different components of Mars. But to create this mosaic, the HRSC crew as an alternative color-referenced every constituent picture to a colour mannequin derived from high-altitude observations, permitting them to protect colour variations and reveal a colour view. a lot richer on Mars than has been seen earlier than, ESA stories.
Mars is known for its reddish colour, attributable to excessive ranges of oxidized iron. However, massive components of the planet seem like fairly darkish and blue-hued within the new mosaic. These are greyish-black basaltic sands of volcanic origin that type darkish, far-reaching layers of sand throughout Mars. They clump collectively as they transfer with the wind, creating towering sand dunes and dune fields inside the affect craters.
Material eroded by water, alternatively, tends to look lighter. The two most typical water-weathered minerals on Mars, clay and sulfate minerals, seem significantly vivid in such coloured compounds; its presence was established by the OMEGA spectrometer on Mars Express. The presence of those minerals signifies that liquid water existed on Mars for a very long time, eroding and altering the rock over time to type main clay deposits akin to Mawrth Vallis (an historic outlet channel not proven on this view however which HRSC famous above).
Mars Express was initially deliberate to final one Martian 12 months, or about 687 Earth days, however it has continued to fulfill and exceed its targets.
Topics