The research collects information from the 47 Spanish face-to-face public universities in 2020, virtually 80% of whose earnings comes from their regional governments and virtually the remaining from public charges and costs. In Spain, greater than 1.3 million younger individuals are learning at college, half of them on face-to-face public campuses.
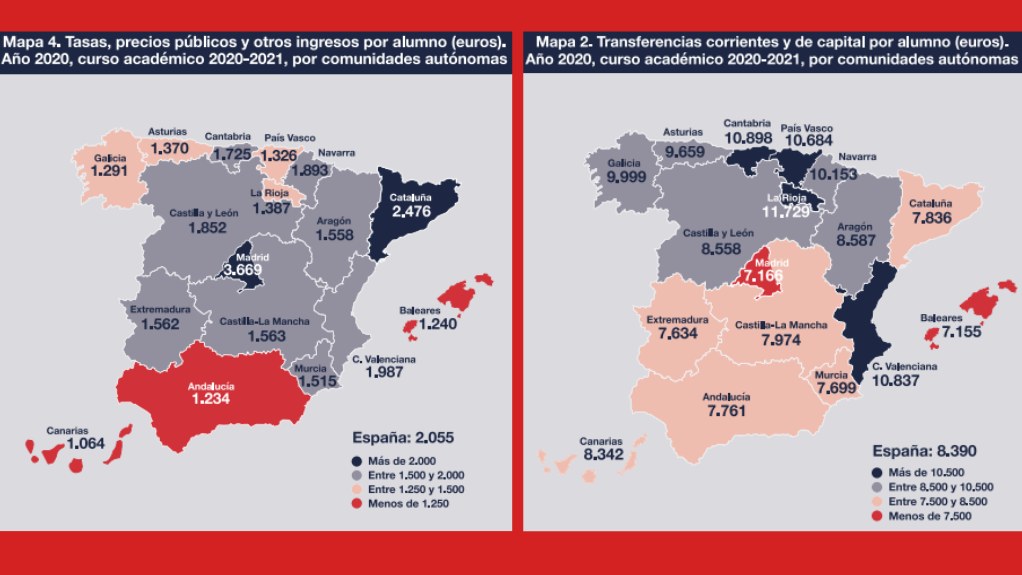
According to the CYD 2021-2022 Report, La Rioja and Cantabria stand out for being the areas that take advantage of transfers to their college students, adopted by the Valencian Community, the Basque Country and Navarra. In these 5 territories, spending per scholar is above 10,000 euros, whereas on the reverse excessive are the Balearic Islands and Madrid, with lower than 7,200 euros per scholar.
Regarding the financing obtained by public campuses considering the extent of wealth within the area -comparing the values of 2020 with these of 2019- all areas elevated the ratio, the place extra within the Valencian Community and the Canary Islands, round 9 factors .
The best effort as soon as once more corresponded to the Valencian Community and Cantabria, accompanied on this event by the Canary Islands, whereas on the opposite aspect are Catalonia and Madrid, explains the doc from the Foundation, chaired by Ana Botín and offered a couple of days in the past. in Madrid.
In the case of the Canary Islands -which in 2019 was in eighth position-, the advance is principally because of the higher drop in GDP per capita in 2020, since, being a extremely touristic area, it suffered extra from the mobility restrictions adopted on account of the pandemic.
The monetary effort of scholars and their households
Regarding the gathering of charges, public costs and different earnings per scholar -that is, the monetary effort of the customers of the system-, within the first three positions seem the Complutense, the Polytechnic of Madrid and the Carlos III, adopted by the Polytechnic de Catalunya, the Autónoma de Madrid and the Politècnica de València, all with values greater than 3,000 euros per scholar.
By areas, Madrid and Catalonia register the very best values within the chapter of taxes, public costs and different earnings in 2020 (as in 2019), whereas within the group of areas with the bottom indicator are the Canary Islands, the Balearic Islands and Andalusia .
With the exception of Madrid, the remainder of the areas suffered setbacks on this indicator in 2020, particularly in Catalonia, principally because of the discount in public college costs.
One of the issues of the college system is the shortage of ample financing, which is why “Spain is systematically under the European international locations and the OECD within the indicator of expenditure per scholar or with respect to GDP, in addition to within the expenditure ratio per scholar with respect to GDP per capita”, underline the conclusions of the report.
Additionally, the evolution for greater than a decade of public funds for greater schooling has been very damaging in Spain. As a results of the sovereign debt disaster, beginning in May 2010, and worsening in 2012, Spain needed to make cuts and improve taxes and charges to attempt to cut back its public deficit.
This additionally affected universities, with decreases in transfers obtained and a rise in public college costs. Despite the enlargement in the course of the 2014-2019 interval, “the figures point out that in 2020 the degrees of 2009 had not but been recovered.”
Given this evolution, the personal participation of households in college financing has tended to extend clearly in proportion phrases, and is now at ranges above these of the OECD.
To attempt to alleviate the monetary insufficiency of the system, the brand new college legislation (LOSU), in parliament, units the target of allocating 1% of GDP to universities.
“This purpose -adds the CYD Foundation- is seen as a name to motion; nonetheless, for its efficient execution it’s worrying that, for now, no binding mechanism has been established to attain it, quite it’s merely the specification of a need to achieve that quantity”. In Spain, public funding for the University is round 0.7% of GDP, whereas in European and OECD international locations it exceeds 1%.